1- SHOCK
Is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body is not getting enough blood flow.
Is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body is not getting enough blood flow.
NURSING MANAGEMENT
Assess level of
consciousness. -
Pulse quality
& rate changes.-
- Fluid
resuscitation.
2- Hemorrhage
A hemorrhage may be "external" and visible on the outside of the body or "internal" where there is no sign of bleeding outside the body.
Nursing
management:
Inspect the wound as a possible site of bleeding.-
Inspect the wound as a possible site of bleeding.-
- Increase IV fluid infusion rate & administer
blood if necessary as soon as possible.
Nursing
management :
- Avoid rubbing
or massaging calves and thighs.
- Encourage leg exercises and ambulate the patient
as soon as permitted by the surgeon.
- Initiate anticoagulant therapy either
intravenously, subcutaneously, or orally as prescribed.
Nursing
management:
- Monitor the
patient’s progress carefully on a daily basis for the first postoperative week
to detect early signs & symptoms of respiratory difficulties.
- Promote full aeration of the lungs.
- Initiate specific measures for particular
pulmonary problems.
5- Pulmonary Embolism ( PE )
Pulmonary embolism is an obstruction of a blood vessel in the lungs, usually due to a blood clot, which blocks a coronary artery.
Nursing
management :
- Administer oxygen
with the patient in an upright sitting position if possible.
- Reassure and quiet the patient.
- Monitor vital signs, ECG, and arterial blood gases.
6- Urinary Retention :
is defined as the inability to completely or partially empty the bladder, Suffering from urinary retention means you may be unable to start urination, or if you are able to start, you can’t fully empty your bladder.
is defined as the inability to completely or partially empty the bladder, Suffering from urinary retention means you may be unable to start urination, or if you are able to start, you can’t fully empty your bladder.
Nursing
management :
- Assist patient
to sit or stand if permissible because many patients are unable to void while
lying in bed.
- Provide the patient with privacy.
- Catheterize only when all other measures are
unsuccessful.
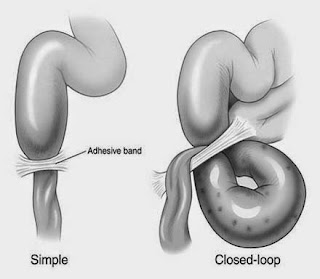
7-Intestinal Obstruction
Intestinal
obstruction occurs when there is a blockage of your small or large intestine.
The blockage prevents the passage of fluid or digested food. The blockage may
be partial or total.
Nursing
management :
- relive abdominal distention by passing a
nasoenteric suction tube.
Replace fluid and
electrolytes.
- Assess bowel tones and degree of abdominal
distention (may need to measure abdominal girth) ;document these findings every shift.
- Monitor and document characteristics of emesis and
nasogastric drainage.
8- Evisceration( wound dehiscence )
extrusion of viscera outside the body, especially through a surgical incision.
Nursing management:
extrusion of viscera outside the body, especially through a surgical incision.
Nursing management:
- Stay with the
patient and have someone notify the surgeon immediately.
- If intestines are exposed , cover with sterile
moist saline dressing .
- Assure the patient that the wound will be properly
cared for attempt to keep patient quiet and relaxed.
9- Wound Infection
Wound infections are caused by the deposition and multiplication of microorganisms in the surgical site of a susceptible host. There are a number of ways microorganisms can get into wounds.
Nursing
management:
- Keep dressing
intact
- Use strict
asepsis when dressing are changed.
- Monitor and document amount type and
location of drainage.
- Ensure that all drains are
working properly.








No comments:
Post a Comment